
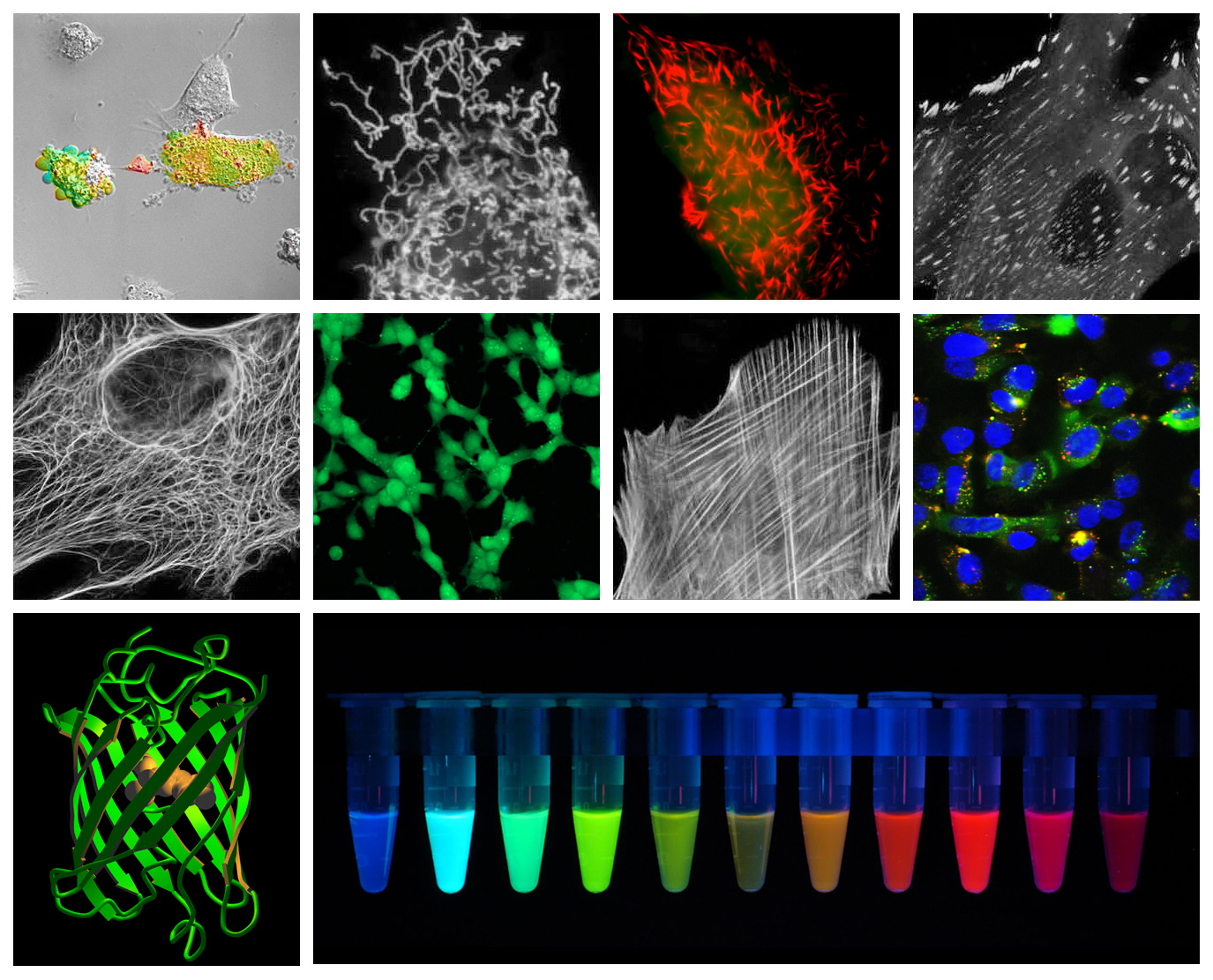
GFP has a wide range of applications and can be used to identify gene expression, dynamics of proteins, organelles and ECM components, in addition to being used as Ca 2 + sensors ( Miyawaki et al., 1997 Nagai et al., 2001), photoactive probes ( Patterson and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2002) phosphory-lation ( Sato et al., 2002), and protein cleavage sensors ( Sato et al., 2002). Analysis has shown GFP to be pH sensitive so additional caution should be used in highly acidic or basic applications. GFP’s stability, together with the general absence of cytotoxic effects (except in very high concentrations ) have lead to its widespread use along with its derivatives. By altering amino acids in the GFP structure mutants have been developed with different emission and excitation wavelengths, including Yellow ( Nagai et al., 2002), Red ( Knop et al., 2002) and Blue ( Heim et al., 1994). Mutants have been developed ( Branchini et al., 1998 Shibasaki et al., 2001) and are widely used to minimize effects but it is still recommended to work quickly when using fluorescent proteins at elevated temperatures. Its major excitation wavelength occurs at 398 nm ( Morise et al., 1974) with a minor absorption at 475 nm ( Ward and Bokman, 1982) GFP is most stable below physiological (37 ☌) temperatures. Its primarily beta barrel structure makes it resistant to ionic quenching via denaturation ( Ward and Bokman, 1982). Green fluorescent protein (GFP) has become one of the most widely known and used fluorescent markers and has been well studied and reviewed ( Zimmer, 2002 Chalfie, 1995 Tsien, 1998). Li, in Characterization of Biomaterials, 2013 Green fluorescent protein This was possible by mutating a serine to threonine at position 65 in the protein sequence ( Heim et al. Number of mutants has been constructed one of them is 5 to 6 times more fluorescent than the wild type. Although this peptide sequence exists in many proteins, none of these peptides display structural and fluorescence characteristics identical to those observed for the peptide sequence in GFP. GFP fluorescence originates from a Ser-Tyr-Gly-sequence that forms a p-hydroxybenzylidene-imidazolidone. The fluorescence maximum is located at 509 nm. Wild type GFP from jellyfish displays an absorption spectrum with two peaks, a major one at 395 and a minor one at 475 nm, with extinction coefficient of 300 M −1 cm −1, respectively. Green fluorescence protein isolated from coelentrates displays a principal function that is to transduce the blue chemiluminescence of the protein aequorin into green fluorescent light by energy transfer. Albani, in Structure and Dynamics of Macromolecules: Absorption and Fluorescence Studies, 2004 3d Relation between fluorescence and a specific sequence in a protein


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
